When it comes to printing PVC plastic ID cards, there are several alternative technologies available, each with its own pros and cons. Here are the most commonly used print technologies for PVC plastic ID cards.
Keep in mind that on-demand card printing involves printing and personalizing individual cards one-by-one, which is quite different from bulk printing of large quantities of identical cards.
Offset Printing
The highest quality printing available is offset printing, however this technology can only be used at the location where the PVC plastic cards are being manufactured. It is the technology used for pre-printing credit cards, gift cards, and in other similar high-volume card issuance situations. It is only appropriate for large runs of cards, where all data is available in advance, with minimum runs of several thousand cards.
Pros
- Extremely clear and precise color definition and color matching
- Durable, long-lasting print quality
- Very low per-card cost
Cons
- Only appropriate for printing where each card is the same
- Minimum quantities per batch are high
- Requires extremely expensive specialized printing equipment
 Direct-to-Card Printing:
Direct-to-Card Printing:
Direct-to-card (DTC) printing, as the name suggests, prints the design directly onto the surface of the PVC card using a thermal print head. This process transfers colored dye or resin-based ink onto the card. During the Direct-to-Card printing process, panels of color ink (generally Y-M-C-K, or Yellow-Magenta-Cyan-Black) are applied directly to the card surface.
Pros
- Fast and efficient printing method
- Suitable for low to medium volume printing
- Allows for full-color printing, including photographs and complex designs, with each card being different
- Generally more affordable compared to other printing methods
Cons
- Lower print quality compared to other printing technologies
- One or more thin white bands which are unprintable on card edges (not fully edge-to-edge)
- Limited color accuracy and inability to reproduce complex gradients.
- Prone to scratching and fading over time.
 Retransfer Printing (also known as Reverse Transfer)
Retransfer Printing (also known as Reverse Transfer)
Reverse transfer printing involves printing the card design onto a clear film, which is then thermally bonded to the PVC card surface using heat and pressure. During the thermal retransfer printing process, panels of color ink are heat-sealed to the specialized substrate in reverse. This substrate then becomes the exterior layer of the card, with the ink sealed between the clear coating and the card body.
Pros
- Provides exceptional print quality, sharpness, and color accuracy
- Can print on various card colors and finishes, including textured cards or cards whose surface is not smooth (like Prox or RFID cards)
- Allows for full-bleed printing, extending the design to the card edges
- Offers excellent durability and resistance to wear and tear
Cons
- Typically more expensive than other printing methods due to specialized equipment and consumables
- Slower compared to direct-to-card printing
- Requires additional steps for film lamination and card application, which can be error-prone and thus result in more re-prints required
You can read more about thermal retransfer in our blog post “Why are your cards so pretty?”
Inkjet Printing:
Inkjet printing involves using inkjet technology to apply liquid ink droplets directly onto the PVC card surface. It typically utilizes pigment-based inks for improved durability. Special inks are required to adhere to the non-porous surface of the PVC card.
Pros
- Relatively inexpensive compared to other printing methods
- Excellent for variable data printing, such as names, serial numbers, or barcodes
- Suitable for printing on different card colors and finishes
Cons
- Lower print quality compared to other technologies, especially in terms of sharpness and color accuracy
- Prone to smudging if not properly dried or sealed
- Limited durability and susceptibility to fading and scratching
Conclusion
Each of these print technologies has its own strengths and weaknesses, so the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements, budget, and desired print quality. Understanding the differences can help you determine whether you can print your ID cards in-house, or need to outsource the printing.
Because InstantCard focuses on (a) on-demand printing of individual ID cards, and (b) highest quality available, InstantCard uses exclusively thermal re-transfer printing for all its card production.
See our FAQ for all other questions regarding ID cards!

 Direct-to-Card Printing:
Direct-to-Card Printing: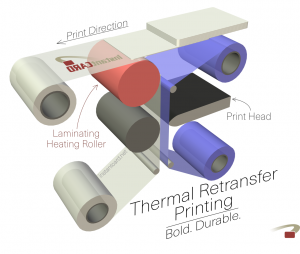 Retransfer Printing (also known as Reverse Transfer)
Retransfer Printing (also known as Reverse Transfer)


